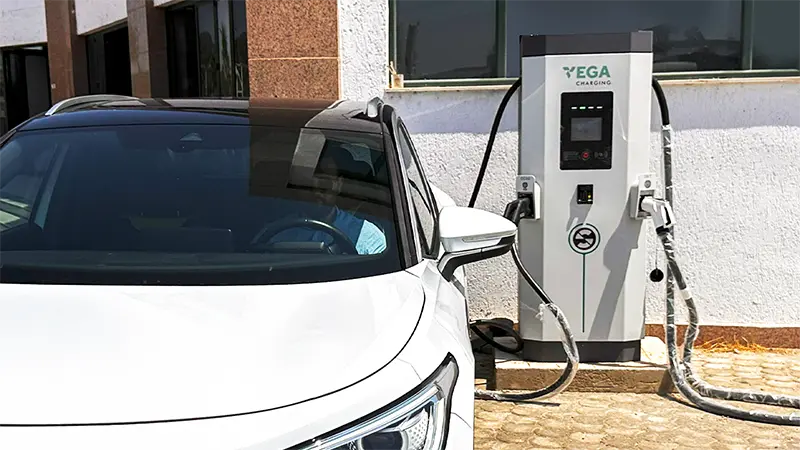

How quickly can you charge an electric vehicle?
One of the most common questions asked by potential electric vehicle (EV) buyers is, “How long does it take to charge an electric car?” Unlike refueling a gasoline-powered car, charging times for EVs can vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for maximizing convenience and planning your daily commutes or long road trips.
This article breaks down the key elements that influence charging times and explains the different types of chargers available to EV owners.
Factors affecting EV charging times
The time it takes to charge an electric vehicle depends on a combination of factors:
1. Battery size
The size of an EV’s battery, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), is one of the most critical factors. Larger batteries can store more energy, which translates to longer driving ranges. However, larger batteries also require more time to charge.
For example, an EV with a 40 kWh battery will charge faster than one with a 100 kWh battery when using the same charger, simply because there’s less energy to replenish.
2. State of charge (SOC)
The SOC refers to how much charge the battery already has when you plug it in. Charging from 0% to 80% is generally faster than charging from 80% to 100% due to battery management systems that slow down charging as the battery nears full capacity.
3. Charger type and power output
The type of charger and its power output significantly impact charging times. Chargers are categorized into three main levels:
- Level 1 (120V): These chargers use a standard household outlet and provide the slowest charging speeds. On average, Level 1 chargers add 3-5 miles of range per hour, making them suitable for overnight charging.
- Level 2 (240V): Level 2 chargers, often found at public charging stations or installed at home, are much faster. They can add 12-30 miles of range per hour, depending on the EV and the charger’s power output.
- DC Fast Chargers (Level 3): These high-speed chargers are typically located at public charging stations along highways. They can charge an EV up to 80% in as little as 20-30 minutes, adding hundreds of miles of range in a short amount of time.
4. Vehicle charging capabilities
Not all EVs can handle the same charging speeds. Some vehicles have a maximum charging rate that limits how much power they can accept, even when connected to a high-power charger. For example, an EV capable of accepting only 50 kW will not charge faster when plugged into a 150 kW DC fast charger.
5. Environmental conditions
Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can impact charging times. Cold weather, in particular, can slow down the charging process as batteries lose efficiency in lower temperatures.
Average charging times by charger type
To better understand the time required to charge an EV, let’s look at some average charging times based on different charger types:
- Level 1 Charger:
- Adds 3-5 miles of range per hour.
- Full charge for a 40 kWh battery: ~40-50 hours.
- Level 2 Charger:
- Adds 12-30 miles of range per hour.
- Full charge for a 40 kWh battery: ~4-8 hours.
- DC Fast Charger:
- Adds 80% charge in 20-30 minutes for most EVs.
- Full charge for a 40 kWh battery: ~1 hour (depending on the vehicle).
The difference between charging at home and on the road
Home charging
Charging at home is the most convenient option for EV owners, as it allows you to plug in your vehicle overnight and wake up to a full battery. Installing a Level 2 home charger is highly recommended for faster charging speeds, especially if you have a long daily commute.
Public charging
Public charging stations are ideal for topping up your battery during errands or on long road trips. DC fast chargers are the go-to option when time is limited, as they provide the quickest boost in range. However, they are generally more expensive per kWh compared to home charging.
Tips to reduce charging time
- Plan ahead: If you know your schedule, charge your EV during off-peak hours or overnight to ensure it’s ready when you need it.
- Invest in a Level 2 charger: Installing a Level 2 home charger can drastically reduce charging times compared to a standard household outlet.
- Use DC fast chargers for road trips: While not ideal for daily use due to cost and potential wear on the battery, fast chargers are perfect for long-distance travel.
- Pre-condition your battery: Some EVs allow you to warm up the battery before charging in cold weather, which can improve charging efficiency.
Final thoughts
The time required to charge an electric vehicle depends on a variety of factors, including battery size, the type of charger used, and the vehicle’s charging capabilities. While charging an EV may not yet match the speed of refueling a gas-powered car, advancements in technology are continuously improving charging times and accessibility.
By understanding how different chargers and factors affect charging times, you can better plan your charging strategy to fit your lifestyle and enjoy the benefits of driving electric.



Leave a comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.